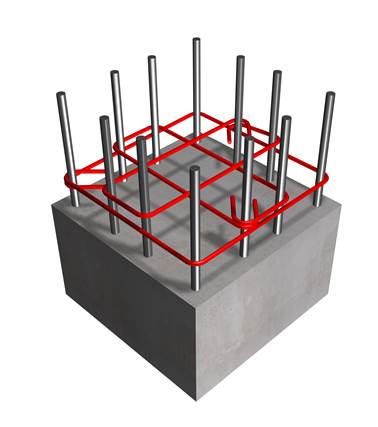
Stirrups constitute one of the most crucial factors affecting the quality and the earthquake resistant strength of buildings.
Three are the major reliability parameters of stirrups:
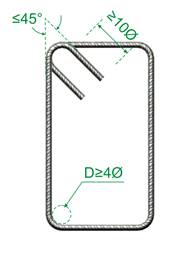
a. The appropriate hooks at its free edges. Hooks are absolutely necessary for the proper behavior of stirrups especially during an intense seismic incident, when concrete spalling occurs, leaving hooks to be the only anchoring mechanism.
b. The pin diameter used for their bending. Stirrups must be bend in rolls with a diameter at least equal to 4Ø, i.e. for Ø 10 they must have a diameter greater or equal to D = 40 mm.
c. The distance between the legs of a closed stirrup. These must be placed no more than 200 mm apart from each other (e.g. a column 500x500 must have three stirrups at each layer).