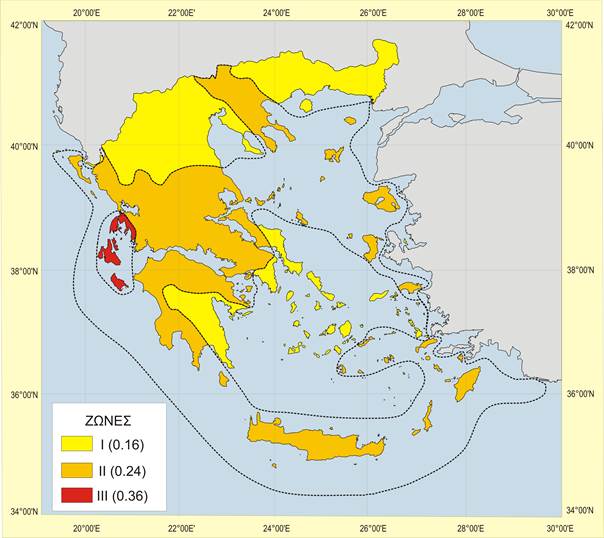
Map of local hazard seismic zones of Greece
The seismic ground vibration is described by the acceleration agR which denotes the reference peak ground acceleration on type A ground.
Each earthquake prone country is divided into Zones depending on the local hazard. A specific reference acceleration agR corresponds to each zone.
For instance, Greece is divided into three zones: Zone 1: agR=0.16g , Zone 2: agR=0.24g, Zone 3: agR=0.36g, where g is the gravity acceleration.